Upper GI Surgery
Ultrasound
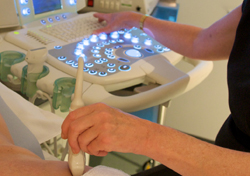
Ultrasound is often used as a means of determining the size, shape and structure of the body's organs, and for detecting any abnormalities.
Examining other organs
Ultrasound is used to examine organs such as the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. An ultrasound scan can detect any abnormalities in these organs such as tumours, gallstones or fluid-filled cysts.
Assisting in complex surgical procedures
Ultrasound technology is frequently used during surgical procedures, such as biopsies (where a tissue sample is taken for analysis). As ultrasound produces clear images of the affected area, it assists the surgeon by ensuring that he or she is working in the right area.
The limitations of ultrasound
Ultrasound waves do not pass through bone, air or gas. Therefore, its use in examining some parts of the body is limited. For example, ultrasound is not ideal for examining the lungs, bowel, stomach and intestines.
Other methods, such as barium tests and CT scans, are more commonly used.

