Vascular Studies Unit |
B56
|
What is EVAR?
What is EVAR?
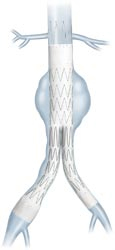
Stent Graft in place in the Aorta
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair or EVAR is a relatively new and less invasive technique for repairing aortic aneurysms. It has been developed over the last ten years and has been the focus of a number of recent clinical trials to assess its safety and efficacy when compared with open surgical repair.
EVAR is carried out by a vascular surgeon and a radiologist who work as a team. The operation is usually performed under a spinal anaesthetic and sedation, recovery time is very quick and patients get back to normal activities much more quickly than with more traditional invasive surgery.
Endovascular means "inside or within a blood vessel". Instead of making a large incision in the abdomen, the doctor makes a small cut near each hip (near the crease between the abdomen and thigh) to get to the femoral arteries (blood vessels).
Through these small cuts, a stent graft (fabric tube) is inserted into the arteries and positioned inside the aorta. This tube usually divides into two limbs at its lower end, like trouser legs.
The endovascular graft seals off the aneurysm at the top and bottom. The graft makes a new path through which the blood flows.
This re-lines the aorta from the inside and prevents blood from flowing into the aneurysm and causing further enlargement and rupture.
Endovascular repair typically takes one to three hours to complete.
Because there are smaller cuts than those in open surgical repair, endovascular repair may result in less discomfort, shorter hospital stay and faster recovery.
Patients may have a hospital stay of only a few days. They can usually return to normal activity within four to six weeks after the procedure.
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)
Next Section: Advantages of EVAR

